Photo from Ed Uthman
Human papillomaviruses (HPV) are non-enveloped, double-stranded DNA viruses which infect human mucosal and epithelial tissues. They survive well in the environment and can be spread through direct contact with a wart, a fomite (ex. doorknob or toilet seat), or when an infant passes through the birth canal. HPV is now the most common sexually transmitted infection in the US1. Even though most infections resolve spontaneously without further progression, it can lead to the formation of skin warts and has been associated with cervical cancer since the 1990s. HPV-6 and HPV-11, two types of HPV, are known to cause genital warts and low-grade cervical abnormalities, while HPV-16 and HPV-18 cause about 70% of cervical cancers. Despite the prevalence and potential severity of this viral infection, there is no specific treatment for HPV. Medical intervention involves treating clinical manifestations of the infection, including removal of warts or cervical neoplasias.
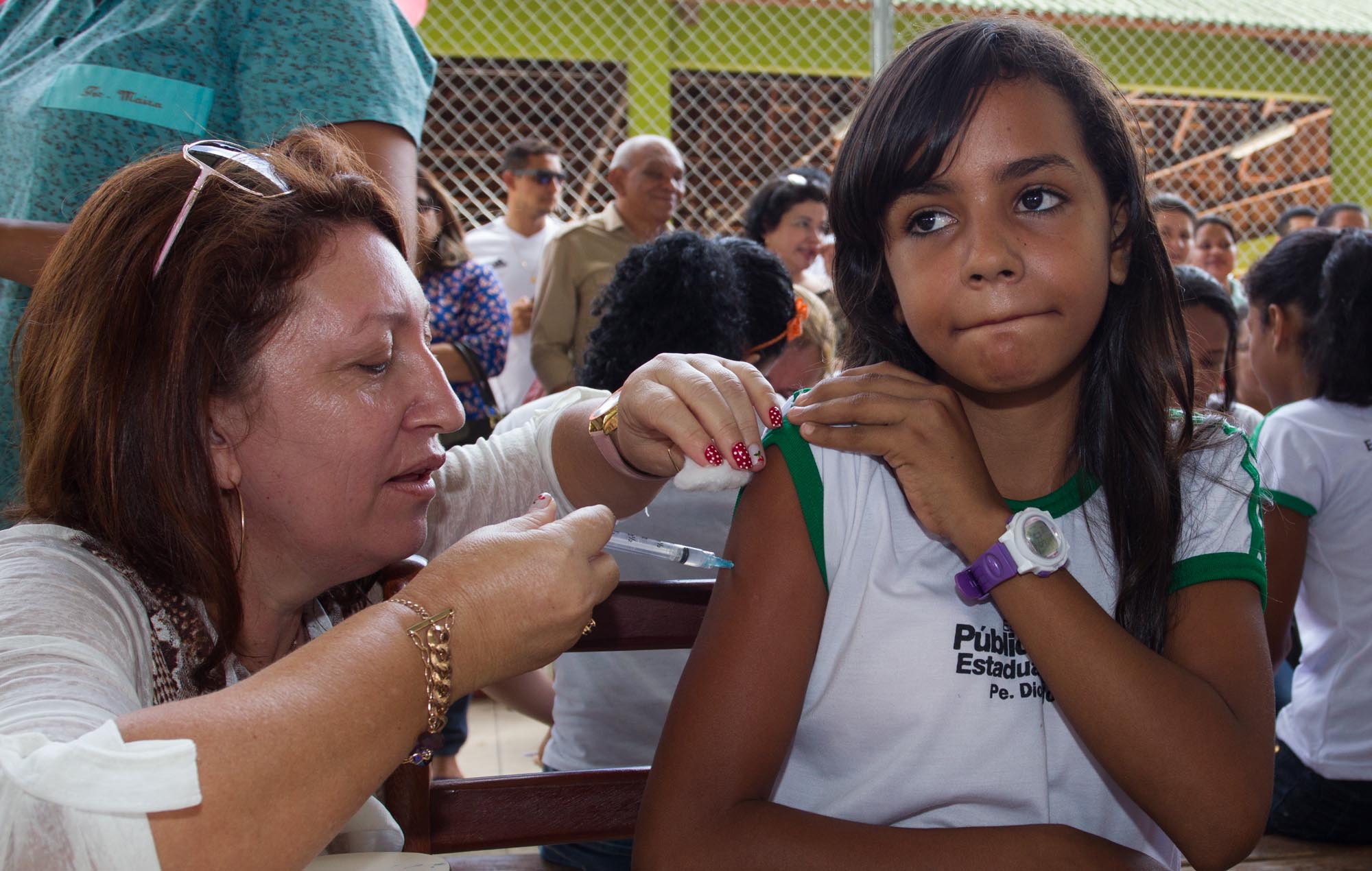
The spread of HPV can be reduced, but not prevented, through the use of condoms and other methods of physical barrier protection. In addition, two new inactivated subunit HPV vaccines, Gardasil and Cervarix, were recently approved by the FDA. The vaccines have no therapeutic effect on those who are already infected and the duration of vaccine protection is unknown, but studies are underway to determine if immunity wanes as time goes by. Both vaccines use the L1 capsid protein, which is produced through recombinant technology. This capsid protein then self-assembles into noninfectious virus-like particles (VLP), which function to elicit a memory immune response.
In 2006, Gardasil, a quadrivalent vaccine (HPV4), was approved by the FDA for both males and females of ages 9 to 26. Gardasil is composed of HPV6, HPV11, HPV 16, and HPV 18 and is administered in a 3 dose course. If a patient has not had all 3 vaccine doses by the age of 26, the remaining rounds can still be administered. HPV4 vaccination is also recommended for all immunocompromised males and men who have sex with men under the age of 26. In 2009, Cervarix, a bivalent vaccine (HPV2) containing HPV 16 and HPV 18, was approved by the FDA. HPV2 is approved for females ages 10 to 25, but is not approved for use in males. Neither HPV4 nor HPV2 contain any preservatives or antibiotics, and more than 99% of those who are vaccinated produce an antibody response to the viral types present in the vaccines. Prior infection with one of the virus types does not diminish the protection against the other types of HPV present in the vaccine.
The vaccines should not be administered to those who are allergic to any vaccine components, are acutely ill, or pregnant women. If a woman becomes pregnant prior to completing the 3-dose vaccination, the remaining doses should be postponed until the completion of the pregnancy. Side effects of HPV vaccination include pain or swelling at the site of vaccination and fever. Overall, no serious adverse reactions have been documented.

Despite the fact that HPV-16 and HPV-18 are highly associated with cervical cancer, controversy has surrounded the HPV vaccines. In general, parents are understandably reluctant to vaccinate their children against a sexually transmitted infection at such a young age, perhaps because the duration of the protection resulting from vaccination is still unknown. Dr. Diane Harper of the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine does not believe the vaccine should be mandated by law since only 5% of women infected with HPV develop cervical cancer2. While that seems valid logically, the basic principle of vaccination is to prepare the body’s immune defenses for eliminating virulent agents before they can lead to harmful medical conditions. As an example, consider poliovirus. Poliovirus affects each individual differently, with up to 95% of the total cases being inapparent or asymptomatic3. Only a small percentage of those who are infected with poliovirus get paralytic polio, the condition which was seen in the public eye so often. Even though infection with poliovirus rarely leads to paralytic polio, parents do not usually hesitate to vaccinate their children in order to prevent this outcome. So, both vaccines prevent a serious outcome which rarely occurs as a byproduct of viral infection, yet polio vaccination has general support around the globe. Despite the fact that the HPV infection doesn’t always result in cervical cancer, parents should not overlook this vaccine, as it drastically reduces the risks of this serious complication even further.
Sources:
1) http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/hpv.html
2) http://www.npr.org/2011/09/19/140543977/hpv-vaccine-the-science-behind-the-controversy
3) http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/polio.html


